
BACKGROUND:
Cancel & replace without the credit
It is in connection with the cancellation of the original contract in replacement of a new contract which has more benefits than the original one, as in upgrading to higher services and also cancel and replace can be for downgrade of services from original contract to a new contract. A new subscription is created as a replacement subscription & for the Canceled subscription customers are not issued any credit/cancellation.
Common scenarios for Cancel & replace without Credit
- Change in contract value with mutual consent.
- Changes in terms of the Contract/products.
- Change to any information other than that affecting the amount e.g.: bill-to information on a posted transaction, this will not impact revenue recognition.
CASE:
ABC Inc, a US-based subscription company has Oracle as their ERP system and enters into a contract with a new customer in France for the sale of services on a subscription basis on 1st Nov-20XX in € Currency. The contract is for a year. The services provided are as mentioned in the below table.
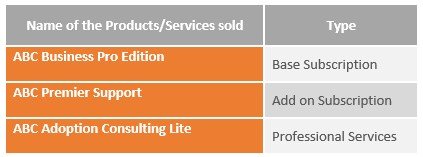
An Add-on is created to increase the quantity by 2 for €0 price as of 8th Nov 20XX on Base subscription.
After the above change customer has applied for cancel & replace without Credit as of 15th NOV-20XX along with a change in Contract Value, change in billing address to US, and change in billing frequency from quarterly billing to annual billing.
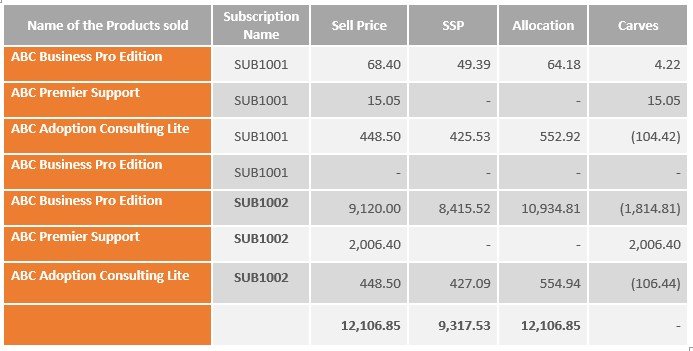
The below table layouts the details of the Old/Original Contract (Canceled Contract) – Subscription Name: – SUB1001
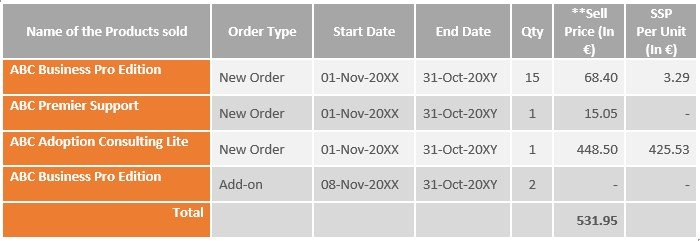
** The Sell price comprises only the billing amount, since it is a no credit case hence, no credit memos/cancellation will be brought against the old contract, and instead of full contract/order value, only the invoiced amount will be considered.
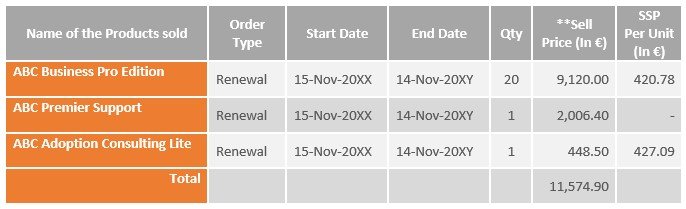
The below table layouts the details of Renewal Contract – Subscription Name: – SUB1002
TREATMENT UNDER ASC 606
So, we will be looking at how the above scenario of credit and rebill is handled under ASC 606.
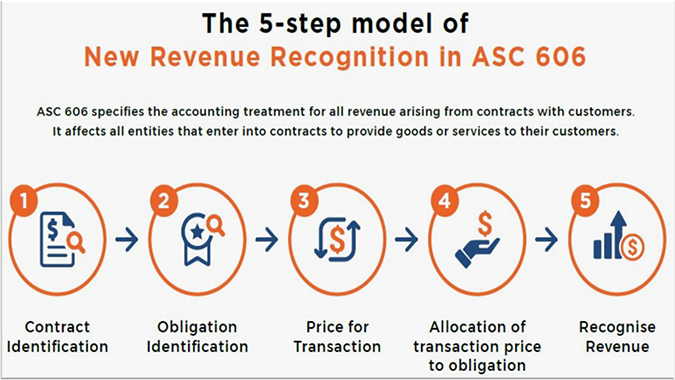
CONTRACT IDENTIFICATION
A contract is an agreement between two or more parties that creates enforceable rights and obligations. This section discusses the steps to determine whether a contract exists and specific considerations that may impact that determination. Each contract will need to go through this evaluation.
Per ASC 606-10-25-1, the five criteria for identifying a contract are as follows:
Assuming, that all the above criteria are satisfied between ABC Inc and the customer for identifying the agreement as a contract.
Combination of Contracts
An entity shall combine two or more contracts entered into at or near the same time with the same customer (or related parties of the customer) and account for the contracts as a single contract if one or more of the following criteria are met:
1. The contracts are negotiated as a package with a single commercial objective.
2. The amount of consideration to be paid in one contract depends on the price or performance of the other contract.
3. The goods or services promised in the contracts (or some goods or services promised in each of the contracts) are a single performance obligation.
In this cancel and replace scenario, ABC Inc will be considering the canceled subscription and the new subscription as a single contract considering their policy of combining contracts based on the customer account number if the subscriptions are created within a reasonable period, like 30 days/90days.
OBLIGATION IDENTIFICATION
A performance obligation is a promise in a contract with a customer to transfer a good or service to the customer. If an entity promises in a contract to transfer more than one good or service to the customer, the entity should account for each promised good or service as a performance obligation only if it is (1) distinct or (2) a series of distinct goods or services that are substantially the same and have the same pattern of transfer.
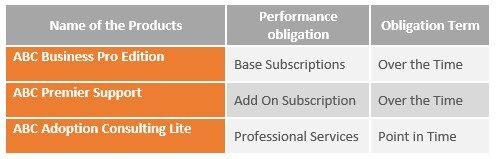
The below table layouts the performance obligations that ABC Inc will identify for the contract
PRICE FOR TRANSACTION
The transaction price is the amount of consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled in exchange for transferring goods or services to a customer, excluding amounts collected on behalf of third parties such as sales taxes. The following items are taken into consideration when determining the transaction price.
- Fixed Consideration (includes consideration related to performance obligations and activation fees)
- Estimated Variable Consideration
- Contingent Amounts (unless no revenue reversal is probable)
- Consideration Payable to the Customer
- Noncash Consideration
- Significant Financing Component
- Amounts Collected on Behalf of Third Parties
- Transaction Price
When determining the transaction price, the Company assumes that the goods or services will be transferred to the customer based on the terms of the existing non-cancellable contract and does not take into consideration the possibility of the contract being canceled, renewed, or modified.
In the case of ABC Inc, the determination of transaction price is straightforward based on what is being charged to the customer i.e. only Fixed consideration.
ALLOCATION OF TRANSACTION PRICE TO OBLIGATION
For a contract that has more than one performance obligation, an entity should allocate the transaction price to in an amount that depicts the amount of consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for satisfying each performance obligation. The performance obligation for allocation will be considered as each distinct separate performance obligation, i.e. let us say there are two separate support services provided within the same contract, even though the performance obligation is the same i.e. “Support”, but for allocation purposes, it will be considered as two separate performance obligation and both the support services will participate in the allocation representing the amount of consideration.
In the case of the Cancel & Replace without credit scenario, for the canceled subscription customer did not get any credit, hence balance revenue will immediately get recognized in the same month in which the cancellation happens.
In the above scenario, cancellation happens in November 20XX, hence revenue for canceled Subscription i.e., SUB1001 for the remaining period will be recognized fully in November
RECOGNIZE REVENUE
An entity should recognize revenue when (or as) it satisfies a performance obligation by transferring a promised good or service to a customer. A good or service is transferred when (or as) the customer obtains control of that good or service. For each performance obligation, an entity should determine whether the entity satisfies the performance obligation over time by transferring control of a good or service over time. If an entity does not satisfy a performance obligation over time, the performance obligation is satisfied at a point in time.
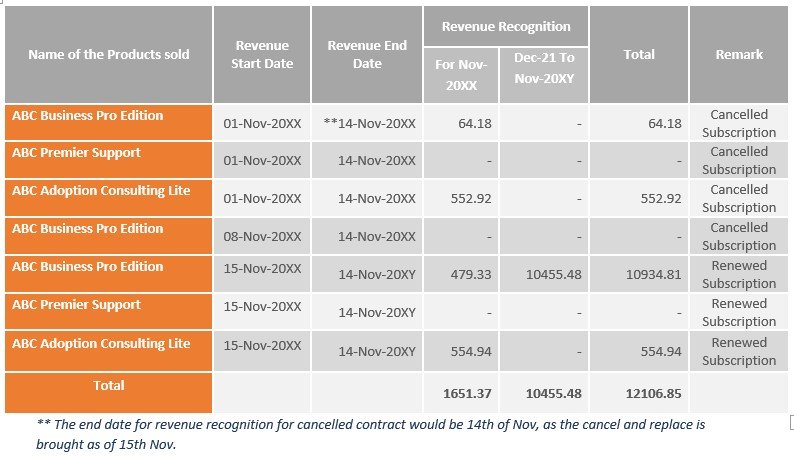
In ABC Inc’s case, subscription SUB1001 is canceled without credit in November 20XX, hence revenue for this subscription has been fully recognized in the same month in which it got canceled and for SUB1002 which is renewed subscription the revenue will be recognized ratably over time i.e., till November 20XY, following is the table in which we have explained how revenue will recognize in the above-mentioned scenario
The below table layouts the revenue recognition for each Performance Obligation (Note: SSP is calculation-SSP per unit * Quantity of Product) (In €)
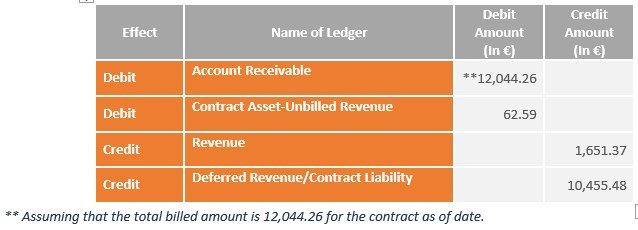
The below table layouts the accounting for November 20XX
Did you find this article on ASC 606 case study helpful? Click here for more Information on ASC 842, IFRS 16, IAS 17, ASC 606 and IFRS 15 or to write to us! We will be happy to answer any questions/queries regarding this and any other topics regarding ASC 842, IAS 17, IFRS 16, IFRS 15, Revenue Recognition and ASC 606.
